

🫒다음회의까지 해야할 일
1. 코드 리뷰 가이드(https://www.notion.so/76fc5e512e0144808acc6fb89769ca11)를 참고하셔서 ⭕️
자신이 강의자인 주차 → 보조자가 올린 해당 주차의 PR 리뷰 ⭕️
자신이 보조자인 주차 → 강의자가 올린 해당 주차의 PR 리뷰 를 진행해주시면 됩니다. ⭕️
(* 자세한 사항은 https://www.notion.so/230730-60347d121c9b4699b65f389659931387 참고하세요) ⭕️
2. epper ppt만들고 이퍼준비클래스에 글 올리기⭕️
앞으로 회의는 일요일 10시로 고정입니다.
[내 목표]
1. 자신이 담당인 주제 2개 중 1개에 대해 라이브코딩 + 필수 + 도전문제 샘플코드 작성하여 PR ⭕️
2. 자신이 보조자인 주제 2개중 1개에 대해 구현문제 샘플코드 작성하여 PR ⭕️
3. 이퍼 PPT 만들기⭕️
4. 코드리뷰하기⭕️
5. 클린코드 공부하기 ⭕️
+ 강의자료 만들기
🫒 코드리뷰


자신이 강의자인 주차 → 보조자가 올린 해당 주차의 PR 리뷰


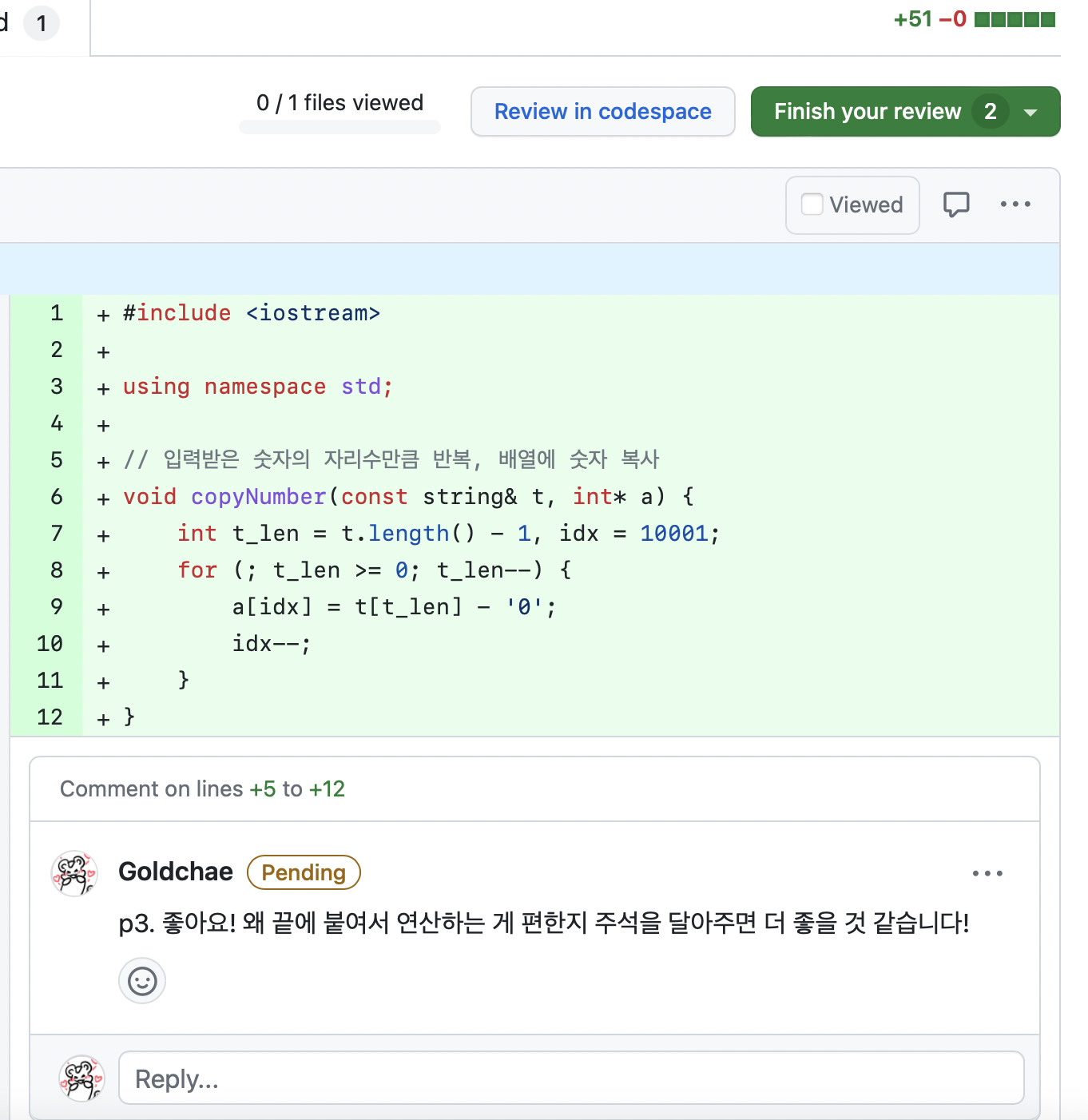
자신이 보조자인 주차 → 강의자가 올린 해당 주차의 PR 리뷰
🫒 클린코드 공부
🧼클린코드🫧 ...ing
알튜비튜에서 코드 리뷰를 위해 공부해봅시다
junggoldchae-coding.tistory.com
🫒이퍼 PPT
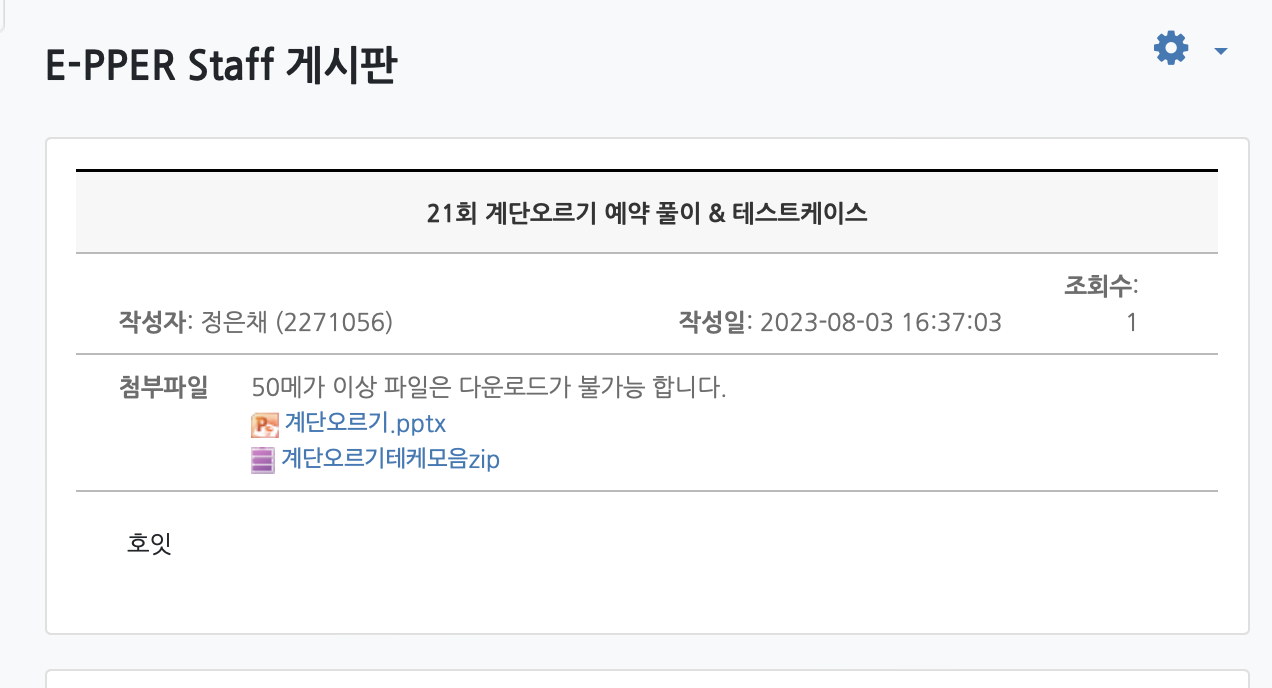

이퍼준비클래스 : https://cyber.ewha.ac.kr/mod/ubboard/view.php?id=1570524
🫒 담당 주차 1개 - 필수문제,도전문제 PR
4기 코드 참고! 선배님들 감사합니다
⭐️ 라이브코딩
백준 1260: DFS와 BFS (실버2 / DFS, BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
vector<bool> visited_recur;
vector<int> dfs(int n, int v, vector<vector<bool>> &edge) {
vector<int> result;
vector<bool> visited (n+1, false);
stack<int> s;
s.push(v);
visited[v] = true;
result.push_back(v);
while(!s.empty()) {
int node = s.top();
bool child = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(edge[node][i] && !visited[i]) {
child = true;
s.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
result.push_back(i);
break;
}
}
if(!child) {
s.pop();
}
}
return result;
}
void dfsRecur(int n, int node, vector<vector<bool>> &edge) {
visited_recur[node] = true;
cout << node << ' ';
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(edge[node][i] && !visited_recur[i]) {
dfsRecur(n, i, edge);
}
}
}
vector<int> bfs(int n, int v, vector<vector<bool>> &edge) {
vector<int> result;
vector<bool> visited (n+1, false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(v);
visited[v] = true;
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
result.push_back(node);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(edge[node][i] && !visited[i]) {
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
return result;
}
int main() {
int n, m, v, n1, n2;
vector<vector<bool>> edge;
// 입력
cin >> n >> m >> v;
edge.assign(n+1, vector<bool> (n+1, false));
visited_recur.assign(n+1, false);
while(m--) {
cin >> n1 >> n2;
edge[n1][n2] = true;
edge[n2][n1] = true;
}
// 연산
vector<int> dfs_result = dfs(n, v, edge);
vector<int> bfs_result = bfs(n, v, edge);
// 출력
for(int i = 0; i < dfs_result.size(); i++) {
cout << dfs_result[i] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
//dfsRecur(n, v, edge);
for(int i = 0; i < bfs_result.size(); i++) {
cout << bfs_result[i] << ' ';
}
return 0;
}백준 2606: 바이러스 (실버3 / DFS, BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
/*
vector<bool> visited_dfs;
void dfs(int node, vector<vector<int>> &graph) {
visited_dfs[node] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) {
int next_node = graph[node][i];
if(!visited_dfs[next_node]) {
dfs(next_node, graph);
}
}
}
*/
int bfs(int n, vector<vector<int>> &graph) {
int cnt = 0;
vector<bool> visited (n+1, false);
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
visited[1] = true;
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) {
int next_node = graph[node][i];
if(!visited[next_node]) {
q.push(next_node);
visited[next_node] = true;
cnt++;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
int main() {
int n, m, n1, n2;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
// 입력
cin >> n >> m;
graph.assign(n+1, vector<int> (0));
//visited_dfs.assign(n+1, false);
while(m--) {
cin >> n1 >> n2;
graph[n1].push_back(n2);
graph[n2].push_back(n1);
}
// 연산 & 출력
cout << bfs(n, graph);
/*dfs(1, graph);
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if(visited_dfs[i]) {
cnt++;
}
}
cout << cnt;*/
return 0;
}백준 7576: 토마토 (골드5 / BFS)
⭐️ 필수
- 백준 4963: 섬의 개수 (실버2 / BFS,DFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int VISITED = 2;
int dr[8] = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1};
int dc[8] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
void dfs(int sr, int sc, int h, int w, vector<vector<int>> &map) { // dfs 탐색
map[sr][sc] = VISITED; // 방문 check
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { // 이어진 땅 없는지 탐색
int nr = sr + dr[i];
int nc = sc + dc[i];
if(nr >= 0 && nr < h && nc >= 0 && nc < w && map[nr][nc] == 1) { // 땅 발견
dfs(nr, nc, h, w, map);
}
}
}
int cntIsland(int h, int w, vector<vector<int>> &map) { // 섬 개수 세기
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 1) { // 땅 발견
cnt++;
dfs(i, j, h, w, map); // (i,j)와 연결된 땅 탐색 (== 섬 만들기)
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
/*
* [섬의 개수 세기]
* 1. 땅을 발견할 때마다 그래프 탐색을 이용하여 연결된 땅을 찾아 섬을 만든다.
* 2. 따라서 그래프 탐색 횟수가 섬의 개수가 된다.
*/
int main() {
int w, h;
vector<vector<int>> map;
while(true) {
// 입력
cin >> w >> h;
if(w == 0 && h == 0) { // 종료조건
break;
}
map.assign(h, vector<int> (w, 0));
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
// 연산 & 출력
cout << cntIsland(h, w, map) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pi;
const int VISITED = 2;
int dr[8] = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1};
int dc[8] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
void bfs(int sr, int sc, int h, int w, vector<vector<int>> &map) { // bfs 탐색
queue<pi> q;
q.push({sr, sc});
map[sr][sc] = VISITED; // 방문 check
while(!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { // 이어진 땅 없는지 탐색
int nr = r + dr[i];
int nc = c + dc[i];
if(nr >= 0 && nr < h && nc >= 0 && nc < w && map[nr][nc] == 1) { // 땅 발견
q.push({nr, nc});
map[nr][nc] = VISITED; // 방문 check
}
}
}
}
int cntIsland(int h, int w, vector<vector<int>> &map) { // 섬 개수 세기
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
if(map[i][j] == 1) { // 땅 발견
cnt++;
bfs(i, j, h, w, map); // (i,j)와 연결된 땅 탐색 (== 섬 만들기)
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
/*
* [섬의 개수 세기]
* 1. 땅을 발견할 때마다 그래프 탐색을 이용하여 연결된 땅을 찾아 섬을 만든다.
* 2. 따라서 그래프 탐색 횟수가 섬의 개수가 된다.
*/
int main() {
int w, h;
vector<vector<int>> map;
while(true) {
// 입력
cin >> w >> h;
if(w == 0 && h == 0) { // 종료조건
break;
}
map.assign(h, vector<int> (w, 0));
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
// 연산 & 출력
cout << cntIsland(h, w, map) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
백준 1325: 효율적인 해킹 (실버1 / BFS,DFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
vector<bool> hacked; // 컴퓨터 해킹 여부 저장
int dfs(int node, vector<vector<int>> &graph) { // node 컴퓨터가 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 개수 세기
int cnt = 1; // node가 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 수
hacked[node] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) { // node 컴퓨터가 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 탐색
int next_node = graph[node][i];
if(!hacked[next_node]) { // 아직 해킹되지 않은 컴퓨터 발견
cnt += dfs(next_node, graph);
}
}
return cnt;
}
vector<int> hack(int n, vector<vector<int>> &graph) { // 가장 많은 컴퓨터를 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 번호 반환
int max_cnt = 0; // 감염된 컴퓨터 수의 최댓값
vector<int> result; // 컴퓨터 번호 저장
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // i : 최초로 해킹된 컴퓨터
hacked.assign(n+1, false); // (탐색 시작전 전역변수 초기화 필요)
int tmp = dfs(i, graph); // tmp : i번 컴퓨터가 해킹한 컴퓨터 수
if(tmp > max_cnt) { // 최댓값 갱신
max_cnt = tmp;
result = {i};
}
else if(tmp == max_cnt) { // 컴퓨터 번호만 push
result.push_back(i);
}
}
return result;
}
/*
* [가장 많은 컴퓨터를 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 번호 구하기]
* 그래프 탐색을 이용하여 컴퓨터별 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 수를 구한다.
*/
int main() {
int n, m, a, b;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
// 입력
cin >> n >> m;
graph.assign(n+1, vector<int> (0));
while(m--) {
/*
* a는 b를 신뢰한다
* == b는 a를 감염시킬 수 있다
*/
cin >> a >> b;
graph[b].push_back(a);
}
// 연산 & 출력
vector<int> result = hack(n, graph);
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i] << ' ';
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int bfs(int s, int n, vector<vector<int>> &graph) { // s번 컴퓨터가 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 개수 세기
int cnt = 1; // s가 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 수
vector<bool> hacked (n+1, false); // 컴퓨터 해킹 여부 저장
queue<int> q;
hacked[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); i++) { // node 컴퓨터가 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 탐색
int next_node = graph[node][i];
if(!hacked[next_node]) { // 아직 해킹되지 않은 컴퓨터 발견
cnt++;
hacked[next_node] = true;
q.push(next_node);
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
vector<int> hack(int n, vector<vector<int>> &graph) { // 가장 많은 컴퓨터를 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 번호 반환
int max_cnt = 0; // 감염된 컴퓨터 수의 최댓값
vector<int> result; // 컴퓨터 번호 저장
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // i : 최초로 해킹된 컴퓨터
int tmp = bfs(i, n, graph); // tmp : i번 컴퓨터가 해킹한 컴퓨터 수
if(tmp > max_cnt) { // 최댓값 갱신
max_cnt = tmp;
result = {i};
}
else if(tmp == max_cnt) { // 컴퓨터 번호만 push
result.push_back(i);
}
}
return result;
}
/*
* [가장 많은 컴퓨터를 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 번호 구하기]
* 그래프 탐색을 이용하여 컴퓨터별 해킹할 수 있는 컴퓨터 수를 구한다.
*/
int main() {
int n, m, a, b;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
// 입력
cin >> n >> m;
graph.assign(n+1, vector<int> (0));
while(m--) {
/*
* a는 b를 신뢰한다
* == b는 a를 감염시킬 수 있다
*/
cin >> a >> b;
graph[b].push_back(a);
}
// 연산 & 출력
vector<int> result = hack(n, graph);
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i] << ' ';
}
return 0;
}⭐️ 도전
프로그래머스 : 게임 맵 최단거리 (Lv.2 /BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pi;
int dr[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dc[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
const int NOT_VISITED = -1;
int bfs(vector<vector<int>> &maps) { // 상대 팀 진영에 도착하기 이해 지나가야 하는 칸의 수 반환
int n = maps.size(), m = maps[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> w(n, vector<int> (m, NOT_VISITED)); // 해당 칸까지 가기 위해 지나가야 하는 칸 수
queue<pi> q;
// 시작점 push
q.push({0, 0});
w[0][0] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
if(r == n-1 && c == m-1) { // 상대팀 진영에 도착한 경우
return w[n-1][m-1];
}
int weight = w[r][c]; // (r,c)까지 이동하는데 지나간 칸의 수
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nr = r + dr[i];
int nc = c + dc[i];
// 다음 칸으로 이동할 수 있는 경우 (== 벽이 아니고 방문한 적이 없는 칸인 경우)
if(nr >= 0 && nr < n && nc >= 0 && nc < m && maps[nr][nc] && w[nr][nc] == NOT_VISITED) {
q.push({nr, nc});
w[nr][nc] = weight+1;
}
}
}
return w[n-1][m-1];
}
int solution(vector<vector<int> > maps)
{
return bfs(maps);
}
/*
* 상대 팀 진영에 도착하기 위해 지나가야 하는 칸의 개수 구하기
* == 최단 거리 구하기
* -> bfs를 이용한다!
*/
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> maps = {{1,0,1,1,1},{1,0,1,0,1},{1,0,1,1,1},{1,1,1,0,1},{0,0,0,0,1}};
// 연산 & 출력
cout << solution(maps);
return 0;
}백준 19538: 루머 (골드4/BFS)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int NOT_BELIEVE = -1;
vector<int> bfs(int n, vector<vector<int>> &adj_list, vector<int> &spreader) {
vector<int> result(n+1, NOT_BELIEVE); // 루머 믿기 시작한 시간
vector<int> adj_believer_cnt(n+1, 0); // 루머를 믿는 주변인의 수
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0; i < spreader.size(); i++) { // 루머 유포자 세팅
int p = spreader[i]; // 루머 유포자 p
result[p] = 0; // (== 루머 유포자는 처음부터 루머를 믿고 있기 때문에 0초 세팅)
q.push(p);
}
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front(); // 루머를 믿는 node
int w = result[node]; // node가 루머를 믿기 시작한 시간
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < adj_list[node].size(); i++) {
/*
* node가 주변인 next_node에게 루머를 유포하고자 한다.
* node가 루머를 믿고 있으므로 루머를 믿는 next_node의 주변인의 수가 증가한다.
*/
int next_node = adj_list[node][i];
adj_believer_cnt[next_node]++; // (== next_node의 주변인 node가 루머를 믿는다)
/*
* [next_node가 루머를 믿기 시작하는 경우]
* 1. 아직 루머를 믿고 있지 않으며
* 2. next_node의 주변인의 절반 이상이 루머를 믿고 있다.
*/
if(result[next_node] == NOT_BELIEVE && adj_believer_cnt[next_node] >= ceil((float) adj_list[next_node].size() / 2)) {
result[next_node] = w+1;
q.push(next_node);
}
}
}
return result;
}
/*
* [루머 유포하기]
* 전제조건 : "주변인의 절반 이상이 루머를 믿을 때 본인도 루머를 믿는다."
* -> 루머를 믿는 주변인의 수를 계산해야 한다.
*/
int main() {
int n, m, p;
vector<vector<int>> adj_list;
vector<int> spreader; // 루머 유포자 번호 저장
// 입력
cin >> n;
adj_list.assign(n+1, vector<int> (0));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // i사람 주변인 입력
while(true) {
cin >> p;
if(p == 0) {
break;
}
adj_list[i].push_back(p);
}
}
cin >> m;
spreader.assign(m, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> spreader[i];
}
// 연산 & 출력
vector<int> result = bfs(n, adj_list, spreader);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << result[i] << ' ';
}
return 0;
}🫒 보조 주차 구현 문제 1개 - 샘플코드 작성 & PR
4기 코드 참고! 선배님들 감사합니다
백준 18111: 마인크래프트 (실버2/구현, 브루트 포스)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int MAX_HEIGHT = 257;
const int INF = 987'654'321;
// 모든 땅의 높이를 height로 만드는 비용 계산
int calcCost(int height, int n, int m, int b, vector<vector<int>>& blocks) {
int cost = 0;
int added = 0; // 추가해야 하는 블록의 총 개수
int removed = 0; // 제거해야 하는 블록의 총 개수
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int gap = abs(height - blocks[i][j]);
if (blocks[i][j] > height) {
// 목표 높이보다 높은 칸인 경우, gap개의 블록 제거
removed += gap;
}
else if (blocks[i][j] < height) {
// 목표 높이보다 낮은 칸인 경우, gap개의 블록 추가
added += gap;
}
}
}
// 전체 비용 계산
cost = 2 * removed + added;
// 블록 개수가 부족하다면 모든 땅의 높이를 height로 만드는 것이 불가능
return (added > (b + removed)) ? INF : cost;
}
// 모든 땅의 높이를 같게 만드는 최소 비용과 그 때의 땅의 높이
pii makeGroundEven(int n, int m, int b, vector<vector<int>>& ground) {
int minCost = INF;
int height = 0;
// 모든 높이를 다 만들어보고 최소 비용 찾기
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_HEIGHT; i++) {
int cost = calcCost(i, n, m, b, ground);
if (cost <= minCost) {
minCost = cost;
height = i;
}
}
return {minCost, height};
}
/**
* 블록 높이의 최댓값이 256밖에 되지 않으므로
* 모든 칸을 높이 n(0~256)으로 만드는 모든 경우를 시도해보고
* 그 중에서 비용이 최소가 될 때를 찾는다.
*
* 모든 칸을 높이 n으로 만드는
*/
int main() {
int n, m, b;
// 입력
cin >> n >> m >> b;
vector<vector<int>> ground(n, vector<int>(m));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> ground[i][j];
}
}
// 연산
pii answer = makeGroundEven(n, m, b, ground);
// 출력
cout << answer.first << " " << answer.second << "\n";
return 0;
}
'Club|Project > 알튜비튜 e-class 튜터 | Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ❇️ 알튜비튜 ❇️ - 8월 2주차 회의 (0) | 2023.08.12 |
|---|---|
| ❇️ 알튜비튜 ❇️ - 8월 1주차 회의 (0) | 2023.08.08 |
| ❇️ 알튜비튜 ❇️ - 7월 4주차 회의 (0) | 2023.07.27 |
| ❇️알튜비튜❇️ - 7월 3주차 회의 (0) | 2023.07.16 |
| ❇️알튜비튜 5기❇️ / 알고리즘 튜터👩🏻🏫 (1) | 2023.05.31 |



